
Can Frogs Hear Sound? The Hearing Abilities of Frogs
Have you ever wondered if frogs can hear sound? Frogs are fascinating creatures that hop around in our backyards or in ponds. They belong to a world filled with sounds, from croaking to the sounds of nature. Understanding how frogs hear is not just interesting; it helps us appreciate their role in the ecosystem. In this article, we will explore how frogs hear, their adaptations to sound, and why it matters to them.
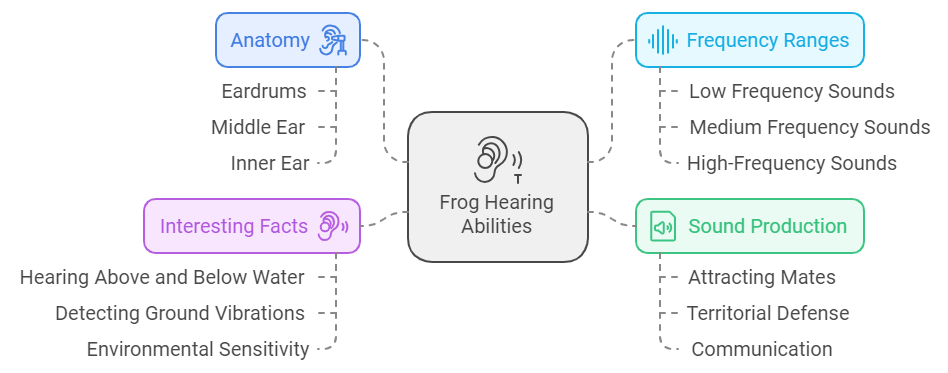
How Do Frogs Hear?
Frogs have a unique way of hearing sound. Here are the main points about their hearing abilities:
- Eardrums: Frogs have external eardrums called tympanums. These are round membranes located behind their eyes. The tympanum vibrates when it hears sound.
- Middle Ear: Behind the tympanum is the middle ear, which processes the sound vibrations. This part allows frogs to amplify the sound.
- Inner Ear: The inner ear contains sensory cells that help frogs interpret sound frequencies.
The Sound Frequencies Frogs Can Hear
The question Can frogs hear sound? leads us to different frequencies. Frogs can hear a range of sounds, but they are especially tuned to certain frequencies. Here’s a table that summarizes the sound frequencies frogs can detect:
| Type of Sound | Frequency (Hz) |
|---|---|
| Low Frequency Sounds | 100 – 300 Hz |
| Medium Frequency Sounds | 300 – 1000 Hz |
| High-Frequency Sounds | 1000 – 4000 Hz |
Frogs primarily communicate in the low to medium frequency range. They often croak or call to each other to find mates, mark territory, or warn of danger. This means that their eardrums are specially adapted to pick up on these specific frequencies.
How Do Frogs Use Sound?
Frogs make sounds for several purposes, and their hearing abilities play a vital role in these activities:
- Attracting Mates: Male frogs croak to attract female frogs—the louder and more attractive the call, the higher the chance of finding a mate.
- Territorial Defense: Frogs use calls to mark their territory. This warns other males to stay away.
- Communication: Frogs communicate with each other through sound. For example, during breeding season, various sounds indicate readiness to mate.
Interesting Facts About Frog Hearing
Here are some amazing facts regarding frog hearing abilities:
- Frogs can hear both above and below water, thanks to their specialized ear structures.
- Some frog species can detect vibrations in the ground, which helps them sense predators.
- Frogs’ hearing can change depending on their environment. For example, it may become more sensitive when they are trying to find a mate.
Conclusion
So, can frogs hear sound? Absolutely! Frogs have excellent hearing abilities that allow them to thrive in their environments. From finding mates to avoiding danger, sound plays an essential role in their lives. Understanding how frogs hear not only enriches our knowledge of these amazing amphibians but also helps us conserve their habitats. Next time you hear a frog croaking, you’ll know it’s a special part of their sound world!
For more information on frog hearing and other fascinating traits, you can visit the National Wildlife Federation’s page here.
